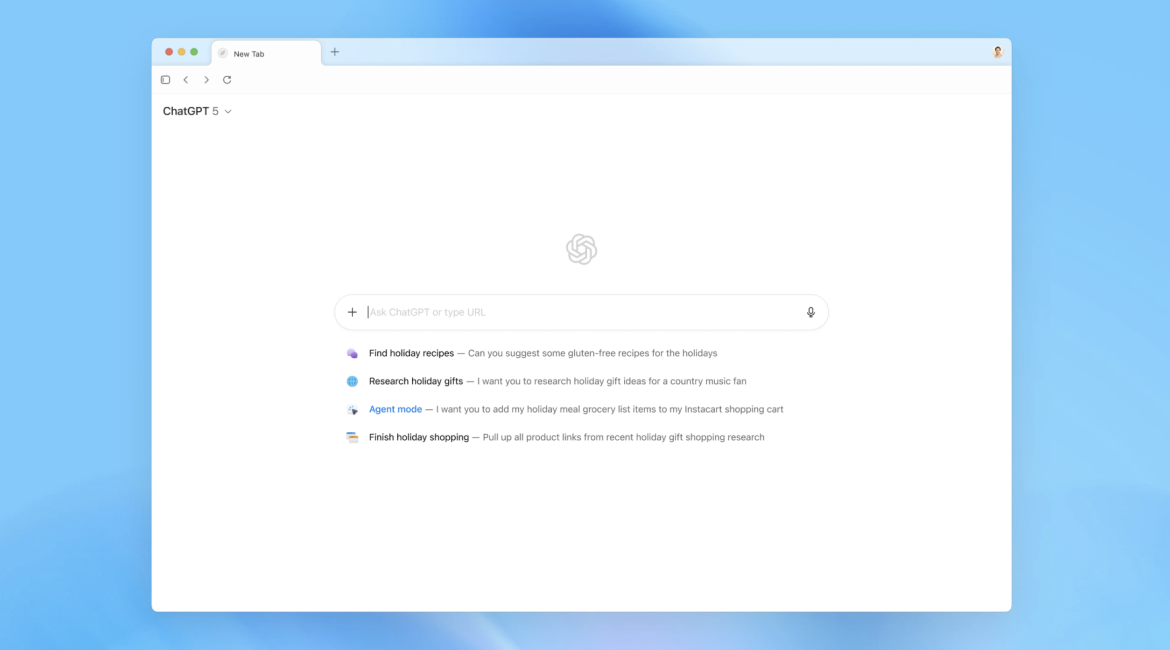
A New Challenger in the Browser Market
OpenAI, the San Francisco–based artificial intelligence company behind ChatGPT, has officially entered the web browser market with the launch of its own browser, ChatGPT Atlas. Designed to compete with giants like Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, the new browser integrates OpenAI’s flagship generative AI model directly into the browsing experience.
For now, ChatGPT Atlas is available exclusively for macOS, but OpenAI has confirmed that Windows, iOS, and Android versions will follow soon.
The browser represents OpenAI’s latest step toward embedding AI assistance seamlessly into everyday digital tools — moving beyond chat interfaces and into how users interact with the web itself.
AI Meets Everyday Browsing
ChatGPT Atlas combines the familiar look and feel of a modern browser — with tabs, bookmarks, extensions, and an incognito mode — but its key innovation lies in how ChatGPT’s capabilities are built directly into the browsing interface.
Instead of merely typing a website address, users can also ask ChatGPT questions or request summaries of the pages they visit. The browser’s sidebar provides real-time AI assistance, offering concise summaries, explanations, and contextual information about any webpage.
For example, if a user opens a long research article or news report, ChatGPT Atlas can instantly produce a readable summary or clarify technical terms — all without switching tabs or copying text into another app.
Smarter Features: Memory and Natural Commands
One of the standout features of ChatGPT Atlas is its Memory Mode. This tool allows the browser to remember users’ browsing history, topics of interest, and previous searches. Over time, it learns from these interactions to offer more personalized and efficient assistance.
Another major innovation is natural language control. Users can simply type or speak commands such as:
-
Clean up my tabs to organize open pages
-
Reopen the shoes I looked at yesterday to revisit previously viewed products
These commands replace complex menu navigation with straightforward conversational prompts, reflecting OpenAI’s vision of a more intuitive relationship between humans and computers.
Competing in an Expanding AI Ecosystem
OpenAI’s move into the browser space comes amid intensifying competition among tech companies integrating artificial intelligence into everyday tools.
-
Google has already merged its AI assistant, Gemini, into the Chrome browser.
-
Microsoft, OpenAI’s close partner, continues to expand Copilot across Edge and Windows.
-
AI-driven search startup Perplexity recently launched its own browser, Comet, blending search and chat capabilities.
Against this backdrop, ChatGPT Atlas could mark a pivotal moment in how users browse the internet. By embedding generative AI at the core of navigation, OpenAI is not only challenging established browsers but also redefining what browsing means in the age of AI.
Implications for the Future of the Web
Experts suggest that tools like ChatGPT Atlas could significantly transform online behavior. Instead of searching and reading through multiple pages, users might increasingly rely on AI to summarize, compare, and extract key information instantly.
Such capabilities could make research, shopping, and news consumption far more efficient — though they also raise questions about privacy, data storage, and the accuracy of AI-generated summaries.
OpenAI has stated that users will have control over memory and privacy settings, allowing them to disable tracking or clear stored data anytime.
Looking Ahead
As AI continues to reshape the digital landscape, the launch of ChatGPT Atlas signals OpenAI’s ambition to expand beyond conversational models into full-fledged platforms.
If widely adopted, this AI-powered browser could influence not just how people interact with information, but also how the web itself evolves — becoming more personalized, conversational, and context-aware.
While it’s too early to predict whether ChatGPT Atlas can rival Chrome’s market dominance, its debut underscores one thing: the next frontier of the internet will be navigated through intelligent, language-driven interfaces.